Overview
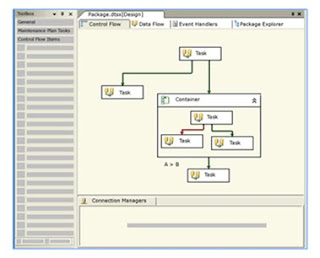
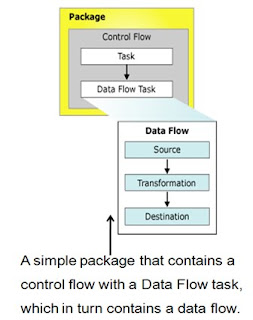
The control flow in a SQL Server 2000 Integration Services (SSIS) package is constructed by using different types of control flow elements.
• Container
• Task
• Precedence constraints
Precedence Constraints
• Precedence constraints connect container and task in packages into an order control flow.
• You can control the sequence execution for tasks and containers, and specify conditions that determine whether tasks and containers run.
• Precedence constraint links two executables:
1 –The precedence executable and
2- The constrained executable.
• The precedence executable runs before the constrained executable and the execution result of the precedence executable may determine whether the constrained executable runs.
Execute SQL Tasks
The Execute SQL task runs SQL statements or stored procedures form a package. Execute SQL task can be used for the following purpose.
• Truncate a table or view in preparations for inserting data.
• Create, alter and drop database objects such as tables and views.
• Re-create fact and dimension tale before loading them.
• Run stored procedures.
Bulk Insert Task
The Bulk Insert task provides the quickest way to copy large amounts of data into a SQL server table or view.You can configure the Bulk Insert task in the following ways.
• Specify the OLE DB connection manager to connect to the destination SQL server database and table or view into which data is inserted.
• Specify the File or Flat File connection manager to access the source file.
• Define the format used by the Bulk Insert task
File System Task
The File System task performs operations on files and directories in the file system.
• All File System task operations use a source, which can be a file or a directory.
• The operations that copy and move file and directories and rename file use destination and a source.